AI-Supported Root Cause Analysis with the Ishikawa Diagram
Reading time: 9min
Table of Contents
Summary
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) helps companies identify the true causes of problems and solve them sustainably. A proven method is the Ishikawa diagram, which structures potential causes into categories such as people, machines, or methods. Brainstorming to identify causes is particularly time-consuming, as numerous factors must be considered and prioritized. Artificial Intelligence (AI) can support this process by recognizing patterns, formulating more precise questions, and analyzing causes. Platforms like Exolynk already use AI to make the analysis process more efficient and to develop well-founded solutions faster.
Introduction
Companies are constantly looking for new ways to quickly identify and resolve problems. Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a crucial step in the problem-solving process, aiming not only to treat symptoms but to identify and eliminate the underlying causes of a problem in a sustainable way. A well-established method for this is the Ishikawa diagram, also known as the fishbone diagram. Combining it with Artificial Intelligence (AI) can optimize and accelerate this labor-intensive process. This article explores what the Ishikawa diagram is, how it is used, which part of the analysis is the most time-consuming, and how AI can assist in brainstorming Ishikawa-related questions.
What is an Ishikawa or Fishbone Diagram?
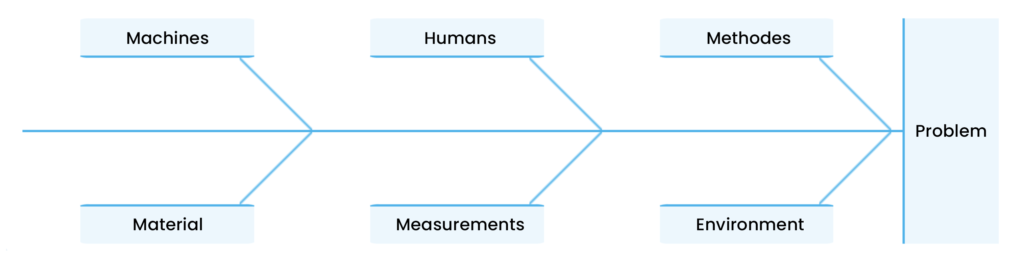
The Ishikawa diagram, named after the Japanese quality management expert Kaoru Ishikawa, was originally developed to improve the quality of production processes. It is a visual representation of causes and effects, helping to identify the root causes of problems within complex systems. The diagram resembles a fish skeleton, hence the name “fishbone diagram.” The “head” of the fish represents the problem or question to be solved, while the “bones” represent different categories of causes that may contribute to the issue.
Example: Ishikawa/Fishbone Diagram
The Ishikawa diagram typically categorizes causes into six main categories, known as the “6Ms”:
- Man (People): Errors or deficiencies caused by human mistakes or insufficient skills.
- Machine: Technical issues or failures of machines and equipment.
- Material: Defects in raw materials or faulty products.
- Method: Problems due to inadequate or inefficient work methods.
- Measurement: Errors or inaccuracies in measuring instruments or methods.
- Milieu (Environment): Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, or other external influences affecting production or performance.
These categories provide a structured and organized approach to identifying causes.
How is the Ishikawa Diagram Used?
The Ishikawa diagram is a valuable tool in many industries, particularly in quality management, process optimization, and failure analysis. Its main advantage is the clear and structured presentation of problem causes, facilitating a better understanding of the underlying issues and helping to develop solutions that address the root cause.
The use of the Ishikawa diagram typically involves several steps:
- Problem Definition: Clearly defining the problem to be solved, such as a quality defect, production delay, or customer complaint.
- Cause Identification: The team identifies potential causes and organizes them into the categories of the Ishikawa diagram. Brainstorming is used to gather all relevant causes.
- Cause Analysis: Once all causes are captured, they are prioritized and analyzed to determine which are most likely contributing to the problem.
- Solution Development: Solutions are developed based on the identified causes, such as process improvements, training, or changes in equipment and work methods.
The Ishikawa diagram encourages an interactive, collaborative approach where all team members can contribute their perspectives. This leads to a broader and more detailed analysis and increases the likelihood of identifying the true cause of the problem.
The Most Labor-Intensive Part of an Ishikawa Analysis
The most challenging part of conducting an Ishikawa analysis is the brainstorming process. During this phase, the team collectively gathers potential causes of the problem and assigns them to the various categories of the diagram. This phase is particularly labor-intensive due to several factors:
- Complexity of Causes: Often, there are multiple interconnected causes of a problem. The team must consider and categorize various potential causes logically.
- Team Dynamics: Successful brainstorming requires active participation and engagement from all team members. Vague or unclear formulations can make it difficult to identify and categorize specific causes.
- Lack of Data: At the beginning of the analysis, concrete data to support cause identification may be missing, making it harder to develop and test hypotheses.
This phase requires creativity, teamwork, time, and patience. The quality of the root cause analysis largely depends on the team’s ability to examine the problem from multiple perspectives.
How AI Can Assist with Brainstorming Ishikawa Questions
Artificial Intelligence (AI) offers new possibilities to accelerate and support the brainstorming process. AI can be a valuable tool for generating ideas, recognizing patterns, and making suggestions that the team might have overlooked.
- Automated Brainstorming: AI tools can analyze large datasets and derive potential causes that could be useful for the team. Through machine learning, AI can learn from historical data and similar problem cases to suggest additional categories and causes. For example, an AI algorithm in a production environment could identify relevant patterns by analyzing past failures.
- Optimizing Questions: AI can also help develop more precise and in-depth questions. By analyzing the team’s inputs based on predefined criteria, AI can highlight specific causes or potential correlations. This allows the team to systematically and efficiently search for the root cause of the problem.
- Analyzing and Prioritizing: AI can pre-analyze and prioritize causes within the Ishikawa diagram. This enables the team to reach a final prioritization faster, with only minor adjustments needed. It becomes easier to focus on the most critical causes and address them effectively.
In summary, AI can greatly support the brainstorming process by simplifying and accelerating it. By automating classification and analyzing large datasets, AI helps teams achieve a well-founded root cause analysis more quickly.
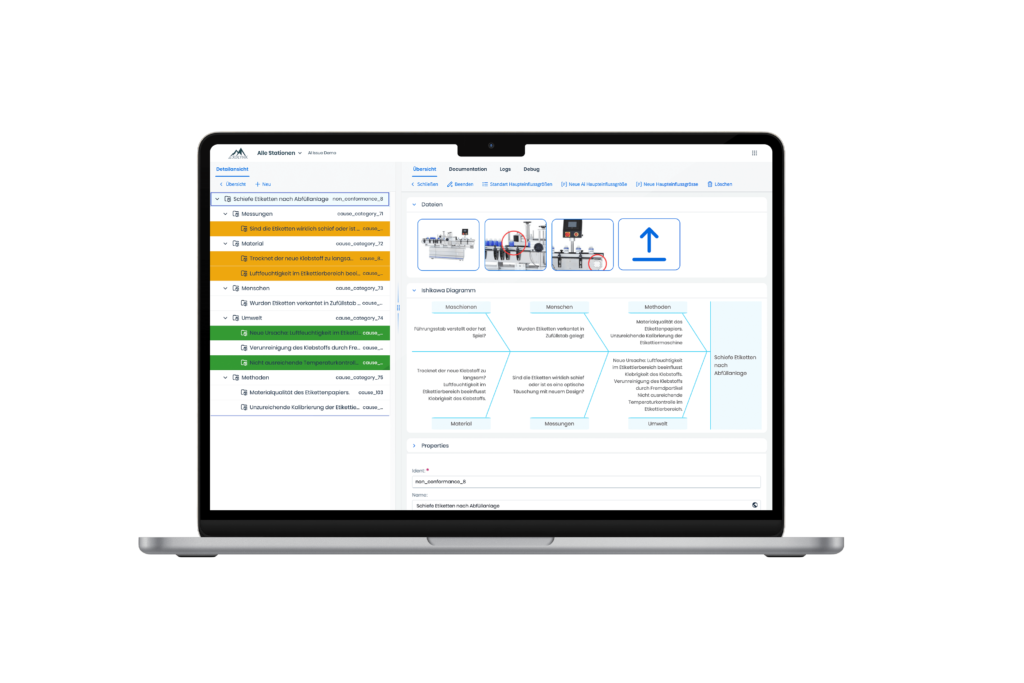
AI-Supported Root Cause Analysis with Exolynk
The Exolynk platform already supports AI-assisted brainstorming for Ishikawa Root Cause Analysis as part of its Non-Conformance and 8D Process offerings. It integrates all collected information on non-conformance, problem descriptions, and 8D processes to generate appropriate suggestions for the brainstorming phase.
Application of Root Cause Analysis (RCA) with Exolynk
We are keen to further develop question optimization and cause analysis in collaboration with customers and partners. This will lead to further productivity gains in quality management and significantly improve the overall quality process.
Conclusion
The Ishikawa diagram is a powerful tool in Root Cause Analysis, helping companies identify and resolve underlying causes of problems. Combining it with Artificial Intelligence provides additional opportunities to optimize the process, especially during brainstorming and cause identification. While brainstorming is often the most labor-intensive part of an Ishikawa analysis, AI can provide valuable support by recognizing patterns, asking deeper questions, and simulating causes. In an increasingly data-driven world, AI is a meaningful complement to traditional methods and can help companies solve problems more quickly and efficiently.